Every PC nowadays has to be an “AI PC”. The NPU determines whether your device falls under this category. Here’s how to check if your work companion is an AI PC or not.
The device used for this manual is set in Dutch. The text has been automatically translated. The exact name of settings may differ on your device.
PC manufacturers are constantly bombarding us with the term “AI PC”. In theory, this is a laptop that can run AI applications locally on the processor, without having to rely on the cloud. In practice, it’s mainly a marketing story to boost sales figures.
Are you curious whether you have an AI PC on your desk? The chance is likely if your device is from this or last year. Almost all new devices coming to market today are promoted as such, whether justified or not. The Copilot key on the keyboard is the simplest indicator, but says nothing about processor power. You can easily do the test yourself.
-
Step 1: Find the Processor
Through Windows settings, you can quickly discover which processor is under the hood of your laptop. Hold WIN + I to open settings and click through to the System menu. Via About (at the bottom of the menu) you get an overview of your device’s specifications.
Our test device, a Microsoft Surface 13, runs on a Qualcomm Snapdragon X Plus. Anyone familiar with processors knows that recent laptops with a Qualcomm Snapdragon processor are recognized by Microsoft as Copilot+ PCs. If you have an Intel or AMD laptop, it depends on which type of processor.
-
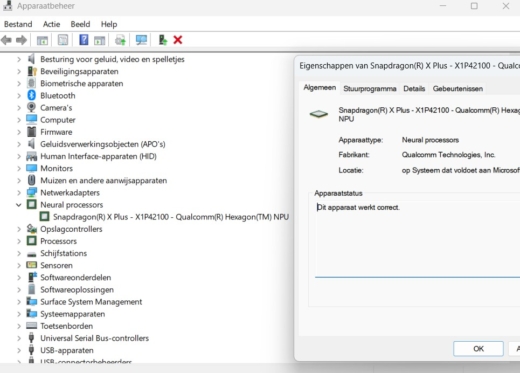
Step 2: Device Manager
The settings don’t tell you if there’s an NPU in your laptop. For this, you need to dive into Device Manager. Two categories are relevant to learn more about the processor. Not surprisingly, these are the menus Processor and Neural Processors. The NPU is under Neural Processors. Click on it to get more information about the chip and update the drivers if necessary.
-
Step 3: Wake up the NPU
Now you know whether you have an AI PC or not. But what is the NPU actually for? At the moment, the NPU has very little work to do in Windows. You’ll notice this if you open Task Manager In the Performance menu, you can monitor the usage of different components.
During typical office work, the NPU graph will show a flat line. The NPU only activates with applications that require local AI computing power. An example is the controversial Recall feature that only works on Copilot+ PCs. Take a screenshot with Recall and you’ll see the spike in NPU usage. Also check the usage when you blur the background in a Teams meeting.
-
Step 4: Run a Benchmark
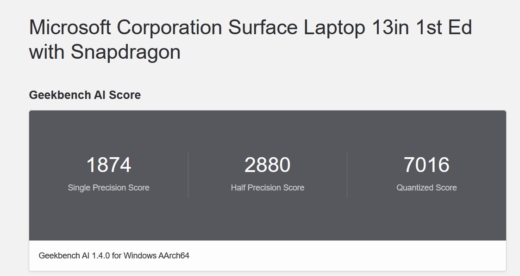
Benchmarks like Geekbench AI provide an estimate of how much AI computing power is in your device. The device tests the CPU, GPU, and NPU, as each component is relevant for processing AI applications. Geekbench AI runs about ten simulations on different types of datasets.
When you open the app, you’ll first see some basic information about your system. Click on Run AI Benchmark to start the simulation. By the time you’ve been to the coffee machine and back to your desk, the simulation will be complete. The scores don’t mean much by themselves, but can be interesting to compare performance between different devices and processors. Geekbench maintains an overview on its website.
Local or in the Cloud?
A regular NPU in an office laptop isn’t very powerful and is barely utilized today. The most popular AI applications like ChatGPT run via your browser in the cloud. ChatGPT won’t work faster on a computer with an NPU.
To run large local AI models, you need a workstation with lots of RAM and a powerful accelerator. The HP Zbook Ultra G1a is an example of a laptop that really has enough horsepower on board to provide a ChatGPT-like experience locally.