AI can promote sustainability by supporting energy efficiency and renewable energy, but it can also lead to increased energy consumption and environmental damage if growth remains uncontrollable. Schneider Electric examines different scenarios and suggests how to move in the right direction.
AI can both promote and undermine sustainability. That is the conclusion of Schneider Electric, based on a comprehensive report that discusses various scenarios. AI’s energy consumption is growing rapidly with the increasing adoption of generative models and the expansion of data centers, leading to both environmental opportunities and risks.
AI as a positive force
AI can contribute to a more sustainable world by facilitating efficient use of energy and resources. In the energy sector, AI can optimize smart grids, integrate renewable energy and balance power consumption in real time.
In addition, AI-driven applications in transportation, logistics and agriculture improve operational efficiency and reduce emissions. Innovations such as energy-efficient hardware, smaller and more fuel-efficient AI models, and advanced cooling technologies help reduce the energy consumption of AI, according to Schneider Electric. In addition, AI can support decarbonization by making processes in industry and buildings more efficient.
Schneider Electric has been vocal about these possibilities of AI for some time. That should come as no surprise. The company specializes in framing data centers with electrical and cooling systems, and also makes power grid solutions. Schneider Electric is making the case here that AI combined with proprietary solutions, can be a positive force.
AI as an undermining factor
AI brings with it a growing energy demand, even Schneider would not deny. The training and inference of Large Language Models are energy intensive. This leads to an increased reliance on data centers, which are often heavy on local power grids.
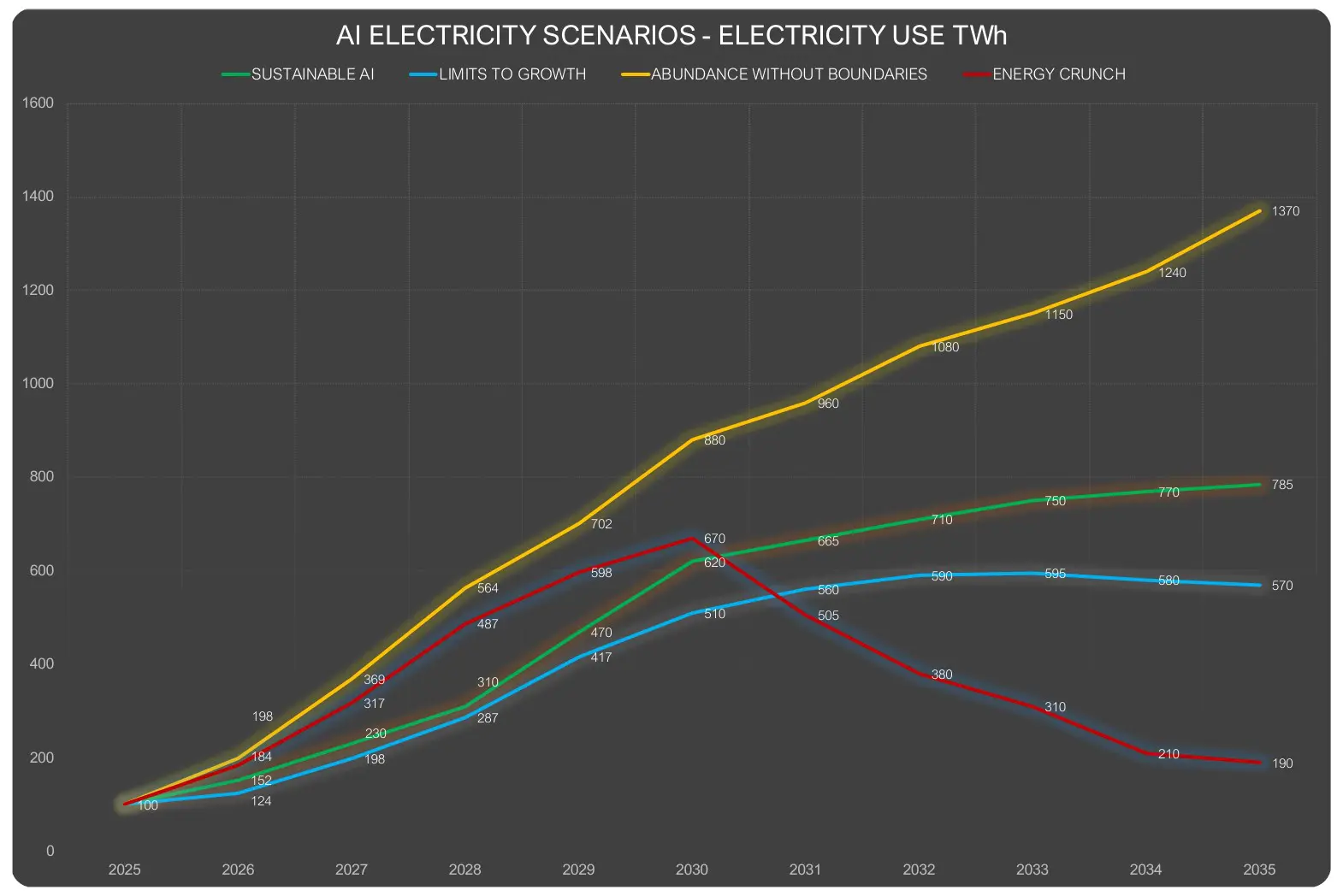
Inefficient use of AI, such as applying large generic models to simple tasks, and unlimited scaling of AI applications can lead to waste and higher emissions. Schneider Electric warns of a future in which AI grows indefinitely, driven by rapid technological advances and unprecedented demand for computing power.
This growth could then lead to an explosion in energy consumption and put significant pressure on the environment, resulting in a concentration of power and inequalities in access to AI technology. Without effective regulation and sustainable infrastructure, this scenario results in waste, environmental damage and a lack of social balance.
Pathway to greater sustainability
Schneider Electric emphasizes that a sustainable future for AI is achievable with targeted measures. Innovations in energy-efficient hardware, algorithmic optimizations and a shift to renewable energy are essential. Regulation, such as certifications for sustainable AI and energy consumption limits, must find wide application. Smart networks, edge computing and efficient data center practices can help relieve pressure on energy infrastructures.
read also
‘AI can greatly advance sustainability and completely undermine it’
If the growth of AI does continue unchecked without regard to sustainability, it could lead to an energy crisis and serious environmental damage. The exponential growth of AI infrastructure could lead to network overloads, local energy shortages and societal resistance to AI, according to the study.
To shift the balance toward a more sustainable future, collaboration between governments, industry and academic institutions is crucial. Policies, innovative technologies and awareness of the environmental impact of AI are indispensable, Schneider Electric suspects. Only by prioritizing efficiency can AI become both the technology of the future and a force for a more sustainable world.
